This all-in-one online Ohm’s Law Calculator performs calculations according to the formula used to calculate the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in an electrical circuit. The electrical power produced by the current in this circuit is also calculated. You can enter the values of any two known parameters in the input fields of this calculator and find the two missing parameters.
V = I·R, P = V·I
Ohm’s Law Formula
Ohm’s law for a circuit section states that the electric current in a circuit section is directly proportional to the voltage and inversely proportional to the electrical resistance of that circuit section.
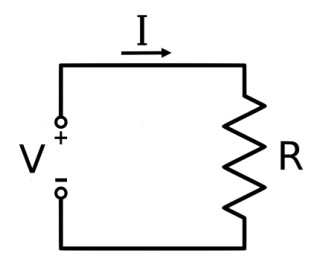
The mathematical equation that describes this relationship is called the Ohm’s law formula:
$$I = \frac{V}{R},$$
where
\(I\) is the current in units of Amperes (A),
\(V\) is the voltage in units of Volts (V),
\(R\) is the resistance in units of Ohms (Ω).
Ohm’s law is true for circuits that contain only resistive elements with no capacitors or inductors. In fact, Ohm’s law states that electrical resistance is constant and independent of current. Conductors, for which Ohm’s law is observed, are called ohmic.
Ohm’s law is an empirical relation that describes well the most common types of conductors in the approximation of low frequencies, current densities and electric field strengths, but is not observed in a number of situations.
Ohm’s law may not be observed:
• at high frequencies,
• at low temperatures for superconductors,
• with strong heating of the conductor by the flowing current,
• in heterogeneous materials.
Electric Power
Electric power is the rate at which electrical energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the Watt (W), 1 W = 1 J/s.
The rate at which resistance in a circuit converts electrical energy into heat is determined by Joule’s Law. Electric power, usually represented by the letter \(P\), produced by an electric current \(I\) passing through an electric potential (voltage) difference of \(V\) is described by the following formula:
$$P = V \cdot I.$$
For a passive linear circuit that obeys Ohm’s law, we can write:
$$P = I^2 \cdot R = \frac{V^2}{R}.$$
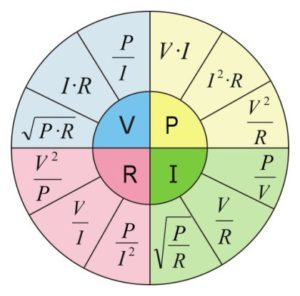
Ohm’s Law Formula Wheel
The combination of Ohm’s law and Joule’s law gives us 12 formulas in which 2 out of 4 variables are known. A summary of all the formulas for these laws is contained in the so-called Ohm’s Law Formula Wheel.
The wheel presented here is a handy tool for calculations. To use it, simply select the quadrant corresponding to the variable you want to calculate, then select the segment corresponding to the variables whose values you know and you will get the necessary formula to calculate.
It is these formulas that are embedded in our Ohm’s Law Calculator, the use of which makes any calculation a matter of seconds.
Related calculators
Check out our other physics calculators such as Work Calculator.