This all-in-one online Voltage Divider Calculator performs calculations using the formula for voltage divider with two resistors, which relates the input and output voltage values to the resistance values of the circuit’s two resistors. You can enter the values of any three parameters in the fields of this calculator and find the missing parameter.
Vout = Vin· R2 / (R1 + R2)
The Formula for Voltage Divider
A voltage divider is a basic electronic circuit that divides an input voltage into two or more output voltages, with the ratio of output voltages determined by the resistances of the circuit’s components. One of the simplest voltage divider circuits is the two resistor voltage divider.
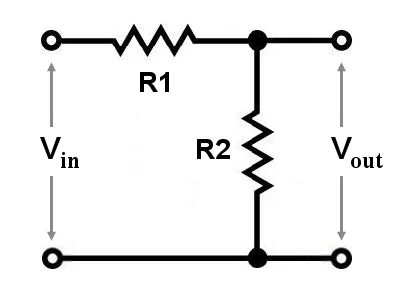
A two resistor voltage divider is a circuit that consists of two resistors connected in series to the input voltage source. The output voltage is taken from one of these two resistors. This configuration is also known as a “potential divider”.
The formula for voltage divider which we use in our Voltage Divider Calculator can be easily obtained using Ohm’s law:
$$V_{out} = V_{in} \cdot \frac{R_2}{R_1+R_2},$$
where
• \(V_{in}\) is the input voltage,
• \(V_{out}\) is the output (scaled down) voltage,
• \(R_1\) and \(R_2\) are the resistor values.
As you can see from this formula, the input voltage decreases to a lower value depending on the ratio of the resistances of these two resistors.
Applications of Voltage Divider
Resistor voltage dividers are commonly used in a variety of applications in electronics. Here are some examples:
• Voltage dividers can be used to measure voltages that are higher than the range of a particular measurement instrument. By using a voltage divider, the voltage can be reduced to a level that is within the range of the measurement instrument.
• In an operational amplifier circuit, a voltage divider can be used to control the gain of the amplifier. By adjusting the resistances of the voltage divider, the gain of the amplifier can be set to a specific value.
• A voltage divider can be used as a logic level shifter to interface two circuits that use different operating voltages. For example, some logic circuits operate at 5V whereas others operate at 3.3V. In this case, a voltage divider might be used to reduce the 5V signal to 3.3V, to allow the circuits to interoperate without damaging the 3.3V circuit.
Related calculators
Check out our other physics calculators such as Ohm’s Law Calculator or Series Resistor Calculator.